If you’re into microcontrollers like me, you should have an FTDI breakout board or the more handy FTDI TTL-232R-3V3 cable. This cable integrates an FTDI USB-to-serial chip and terminates into a 6-pin header, with TTL in/outputs, ready to be interfaced to any microcontroller.
Recently I had to talk to an RS232 port. The voltage used by the RS232 port is anywhere from 7 to 15V (typically), and uses both positive and negative voltages, which cannot be directly interfaced with TTL. Most of my university friends who took microcontroller class previously bought an RS232-to-USB converter, since that’s what the trainer board (evaluation board) uses, but not me. So what should I do now?
Using a MAX232 (actually a HIN232) chip and 5 capacitors, I followed the recommended application circuit to build a level shifter. I laid out the circuit on a veroboard with a 6-pin header on one end for the TTL-232R-3v3 cable, and a 2×5 header for the RS232 port.
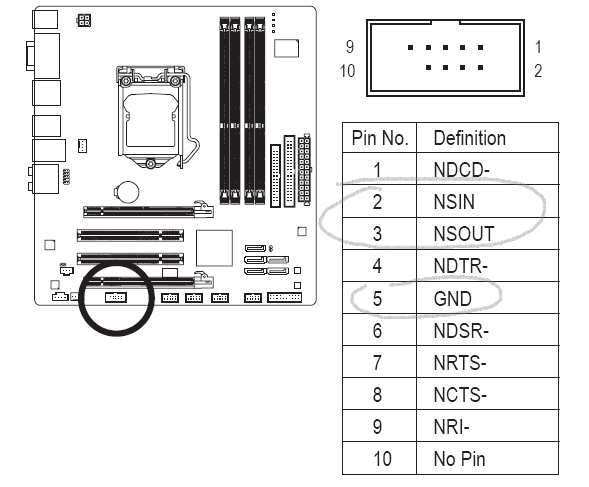
Since I ripped out many old computers with those serial port headers I decided to use it. The pinout for the RS232 port header is available in many motherboard manuals, including mine. The only pins (usually) of interest are circled. The pins are 2, 3 and 5 for receive, transmit and ground, respectively.